Accelerate Your Drug Discovery with QPS Preclinical Pharmacology

Preclinical pharmacology studies are a crucial component of drug development that occurs before a potential drug candidate is tested in humans (clinical trials). These studies aim to assess the efficacy, safety, and pharmacological properties of a drug in non-human subjects, typically in laboratory animals. The animal facility of QPS has been continuously AAALAC accredited since its inception. This industry standard quality seal, combined with over 20 years of deep scientific expertise and a vast amount of historic data, are a clear asset for our clients who range from international biotech and pharma companies to academia and other non-profit organizations.
All of the QPS pharmacology models have been carefully developed in-house and have been both well characterized and well validated. To support our clients in the best possible way, QPS offers in vivo research models as well as biochemical and histological analyses. Our focus on agility and flexibility enables us to use or adapt existing models or establish new models specific to your research focus. We assist with designing a development plan for your small molecules or biologics, and together with our DMPK and Toxicology colleagues, we help you develop custom-built research solutions to get to market faster.
Pharmacology Models Available Today
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), previously known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), is a severe form of Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which was formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Mouse Gubra Amylin MASH (GAN) Diet-induced MASH Model
- Groups of 8 male C57BL/6J mice 6 weeks of age.
- Mice are fed with Gubra Amylin NASH (GAN) diet ad libitum for 28 weeks and treated with vehicle (0.5% CMC), test article, or reference drug via oral gavage once daily for 12 weeks starting from Week 16 to Week 28.

Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), previously known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), is a severe form of Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which was formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
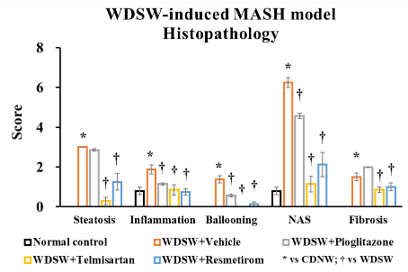
Mouse Western Diet and Sugar Water-induced MASH Model
- Groups of 8 male C57BL/6J mice 8 weeks of age.
- Mice are fed ad libitum a high-fat, high carbohydrate Western diet (WD) containing 42% kcal from fat and 0.2% cholesterol. Mice also receive a high fructose-glucose solution. This combination is referred to as Western diet sugar water (WDSW).
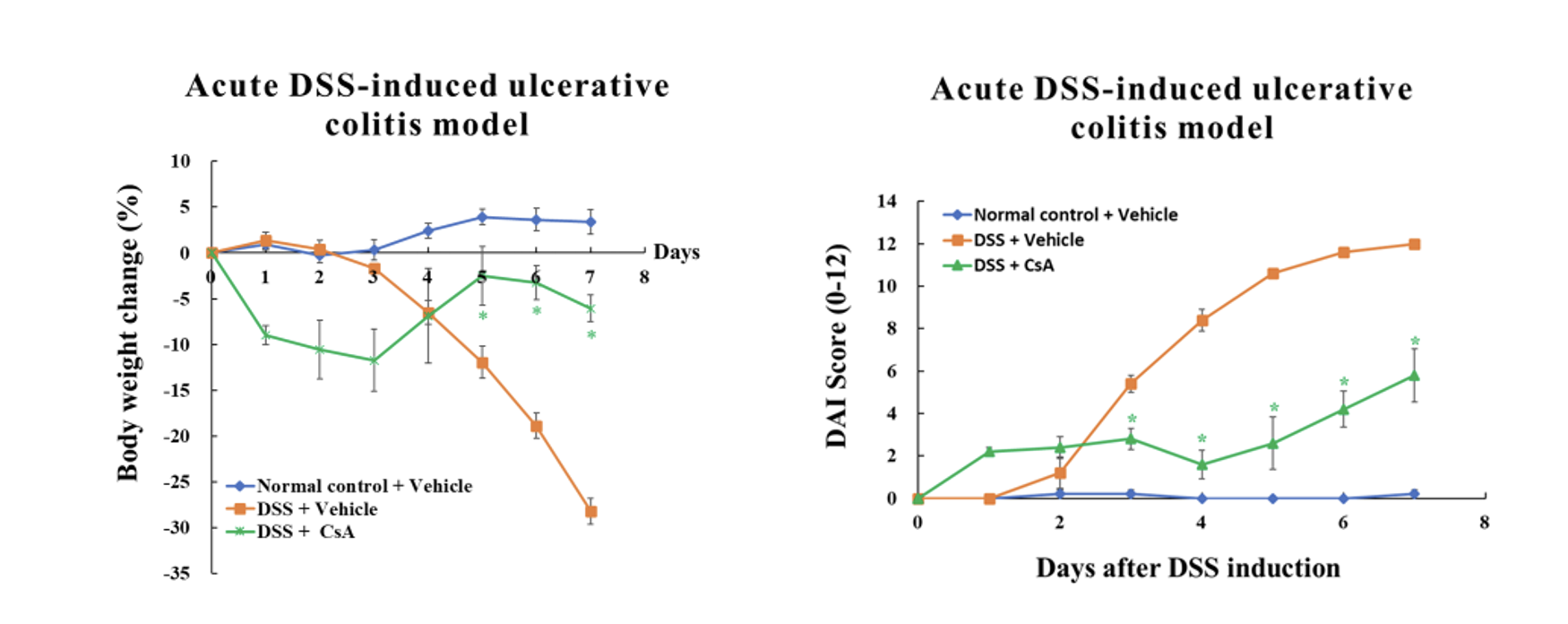
Dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) colitis is the most widely used experimental murine model of ulcerative colitis (UC), established through the administration of DSS in drinking water. The acute DSS-induced UC model is used to evaluate the therapeutic effects of a test article.
Acute DSS-induced Ulcerative Colitis (UC) Model
- Groups of 5 female mice ages 8-9 weeks old.
- DSS is given in autoclaved drinking water for 8 days. The mice in the normal control group are given drinking water.
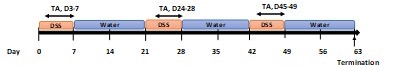
Dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) colitis is the most widely used experimental murine model of ulcerative colitis (UC), established through the administration of DSS in drinking water. The chronic DSS-induced UC model is used to evaluate the therapeutic effects of a test article.
Chronic DSS-induced Ulcerative Colitis (UC) Model
- Groups of 5 female mice ages 8-9 weeks old.
- DSS is given in autoclaved drinking water for 7 days in each cycle, followed by a recovery period of 14 days with normal drinking water, which is repeated for a total of 3 cycles. The mice in the normal control group are given drinking water. The starting day of DSS is D0
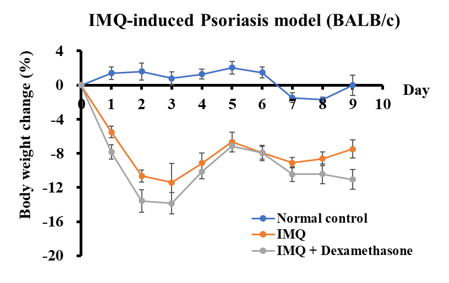
Psoriasis is a chronic recurrent inflammatory skin disease with a complex pathogenesis. Imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis model is used to evaluate the therapeutic effects of a test article
Imiquimod (IMQ)-induced Psoriasis Model
- Groups of 5 female BALB/c mice 8-9 weeks old.
- One day prior to the IMQ application, all animals are anesthetized for fur removal on their backs and ears
Explore Pharmacology Study Details
Why QPS for Pharmacology Studies?
KNOWLEDGEABLE EXPERTS
Knowledgeable Experts
Regulatory Submissions
Regulatory Submissions
Good Laboratoty Practices
Good Laboratory Practices
The QPS Pharmacology Units Consists of the Following Research Facilities

The QPS Pharmacology Units Consists of the Following Research Facilities
Animal Facility
- Housing a wide range of animals to meet your study needs
- Biosafety level 1 and 2 housing (BSL1 and 2)
In vivo Research Laboratory
- Animal treatment and surgery (BSL1 and 2)
- Tissue sampling
Cell Culture Laboratory
- BSF1 and 2 laboratories
- Automated cell and tissue culture image processing hard- and software
- Cutting edge evaluation equipment
Biochemistry Laboratory
- Protein biochemistry laboratory outfitted for cutting edge techniques including aggregation studies
- State-of-the-art equipment for biochemical determinations (fluorometry, densitometry) including biomarker evaluations (MSD imager and others)
Histology Laboratory
- Fully equipped histology laboratory for all fixation, tissue processing, sectioning, and staining
- Modern image capture equipment
- State-of-the-art image processing hard- and software
Key Aspects of Preclinical Studies
Efficacy Evaluation
- In vitro efficacy tests: to study the mechanism of action of active ingredients on biological systems and their release, which are essential for demonstrating the efficacy of active ingredients for medicines.
- In vivo efficacy tests: Utilize relevant animal models to simulate the disease or condition the drug is intended to treat. Assess the drug's efficacy in terms of its ability to produce the desired therapeutic effects.
Safety Assessment
- Toxicology Studies: Evaluate the potential toxicity of the drug by administering varying doses to animals over a specified period. This helps identify any possible adverse effects and establishes a safe starting dose for clinical trials.
- Dose-Response Relationships: Determine the relationship between the dose of the drug and its effects. This is crucial for establishing appropriate dosing regimens.
Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD)
- PK Studies: Investigate how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated by the body. This helps in understanding how the treatment processed by the body.
- PD Studies: Explore the drug's effects on the body and its mechanism of action. This includes assessing the drug's interaction with its target receptors or enzymes.
- Cutting edge evaluation equipment


Formulation Studies
- Dosage Forms: Evaluate different formulations of the drug, such as tablets, capsules, or injections, to identify the most effective and well-tolerated form.
Reproductive and Developmental Studies
- DART studies are designed to reveal any effect of the pharmaceuticals on mammalian reproduction relevant for human risk assessment. Set of studies to cover the stages of reproduction including fertility test to access effects on male and female fertility (FEED), embryonic and fetal development (EFD), and pre- and post-natal development (PPND).
Special Population Studies
- Geriatric and Pediatric Studies: Evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug in specific populations, such as the elderly or children.
ADME Studies
- Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion: Examine how the drug is processed within the body and whether it accumulates in specific organs or tissues.

Contact Us
Ready to accelerate your drug development with QPS Pharmacology services?
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you develop a custom-built research solution.
Visit: https://www.qps.com/
Set Up a Meeting: https://www.qps.com/contact
Email: info@qps.com





