Chronic pain affects more than one-quarter of adults in the United…
Category: Neurology
Home / Neurology
Three separate research studies point to a small protein, platelet-derived chemokine…
In announcing positive results from a trial evaluating donanemab, Eli Lilly reported that…
With a deep brain stimulation device called a “memory prosthesis,” researchers…
What happens in the brain on the verge of death? For…
Building on previous research that showed how epidural electrical stimulation (EES)…
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease, are…
Human brains consist of around 86 billion neurons that connect and…
As many as 30,000 people in the United States are currently…
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia, affecting…
Scientists have spent decades working to understand how spiders spin their…
A large team of researchers has made great strides in developing…
According to the Global Burden of Disease study, 6.2 million patients…
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that causes neurons…
Discovering effective and safe new drugs depends on a detailed knowledge…
The common marmoset, Callithrix jaccus, possesses complex social behaviors and sleep…
In the April 27th issue of JAMA Neurology, researchers released new data that…
According to a study published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia, cognitive decline…
Researchers have designed an antibody that can identify toxic particles that…
RNA sequencing studies of thousands of post mortem human brain samples…
Introduction Researchers are developing novel, safer treatments for cancer, but bringing new oncology therapies to market is challenging. This white paper will examine the…
Introduction As global obesity rates continue to rise, the search for effective treatments is more critical than ever. Obesity is associated with an increased…
Introduction Changes in how clinical trials are managed in the European Union (EU), mandated by the European Union Clinical Trial Regulation 536/2014 (EU CTR),…
NEWARK, Del.—(BUSINESS WIRE)—QPS India, a subsidiary of QPS Holdings, LLC (QPS), a GLP/GCP-compliant global full-service Contract Research Organization, has achieved another significant milestone by…
TAIPEI, Taiwan—(BUSINESS WIRE)—QPS, a leading global contract research organization (CRO) specializing in preclinical and clinical drug development services, is pleased to announce the expansion…
QPS India has achieved another significant milestone by successfully completing a scheduled inspection by the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) from…
Webinars
Using Brain Waves to Detect Pain
August 14, 2024
Chronic pain affects more than one-quarter of adults in the United States. This debilitating level of pain is difficult to treat for a number of
PF4 Offers Hope for Rejuvenating Aging Brains and Combatting Cognitive Decline
November 13, 2023
Three separate research studies point to a small protein, platelet-derived chemokine platelet factor 4 (PF4), as a possible tool for combating cognitive decline in aging

Donanemab Shows Promise in Slowing Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease
July 10, 2023
In announcing positive results from a trial evaluating donanemab, Eli Lilly reported that the monoclonal antibody drug slowed cognitive decline among people with Alzheimer’s disease. The study

Could Deep Brain Stimulation Restore Memory After Brain Injury?
June 28, 2023
With a deep brain stimulation device called a “memory prosthesis,” researchers hope that they may one day be able to improve memory in people who

Research Examines the Mystery of End-of-Life Brain Activity
June 19, 2023
What happens in the brain on the verge of death? For hundreds of years, stories told by people who have come back from the brink

Research Reveals How Epidural Electrical Stimulation Helps People Walk Again
April 3, 2023
Building on previous research that showed how epidural electrical stimulation (EES) can help restore walking ability in people with spinal cord injuries, neuroscientists have now
The Gut-Brain Connection in Alzheimer’s Disease
March 27, 2023
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease, are often associated with the build-up of cellular debris, like misfolded proteins, within the brain.

Reporting Live From the Brain — Tiny Microscope Tracks Activity in Moving Mice
December 5, 2022
Human brains consist of around 86 billion neurons that connect and communicate with each other, forming an intricate network. Understanding how the human brain functions
Brain Implant Enables Communication in ALS Patient
June 29, 2022
As many as 30,000 people in the United States are currently diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS. This debilitating neurological condition is caused by
Immune Response Pathway a Possible Target to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
June 6, 2022
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia, affecting more than 50 million people globally. Projections show that, without a medical intervention, rates

Could Spider Webs Teach Us About Complex Brain Systems?
December 20, 2021
Scientists have spent decades working to understand how spiders spin their impossibly detailed, symmetrical webs. Despite those years of research, scientists remain baffled as to
Consensus Drives Collaboration: In-Depth Cell Analysis Can Accelerate Understanding of the Brain
December 13, 2021
A large team of researchers has made great strides in developing a census and atlas of the cell types found in the mammalian primary motor

Natural Killer Cells May Play a Role in Preventing Parkinson’s Disease
April 12, 2021
According to the Global Burden of Disease study, 6.2 million patients live with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and this number is expected to double by 2040.
Brain Iron Deposits as a Predictive Measure of Dementia in Parkinson’s Disease
January 4, 2021
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that causes neurons in the area of the brain that controls movement to weaken or die. Up
Advances in Drug Discovery for Central Nervous System Diseases
December 7, 2020
Discovering effective and safe new drugs depends on a detailed knowledge of disease mechanisms, as well as a successful progression from candidate identification to clinical
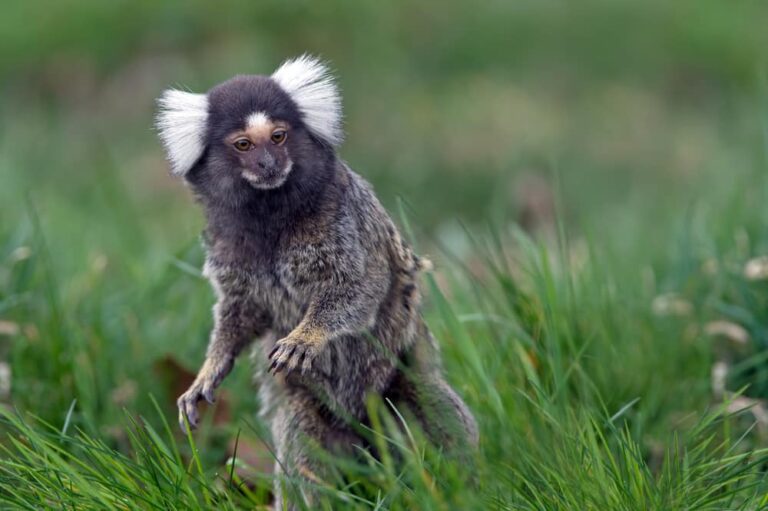

Marmosets as Primate Models of Familial Alzheimer’s Disease
September 28, 2020
The common marmoset, Callithrix jaccus, possesses complex social behaviors and sleep patterns that closely resemble those of humans. This South American monkey’s metabolism, immune systems,
Flortaucipir PET Shows Promise in Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
July 1, 2020
In the April 27th issue of JAMA Neurology, researchers released new data that suggests 18F-flortaucipir positron emission topography (PET) can help clinicians diagnose late-stage Alzheimer’s Disease (AD).

Repetitive Negative Thinking Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease
June 29, 2020
According to a study published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia, cognitive decline and the deposition of harmful proteins in the brain linked to Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)

Research Breakthrough: Antibodies for the Quantification of Amyloid Beta Oligomers in Alzheimer’s Disease
June 22, 2020
Researchers have designed an antibody that can identify toxic particles that destroy healthy brain cells. A collaboration of scientists from the University of Cambridge, University

Proteomic Analysis Studies in Alzheimer’s Disease and Cerebral Atherosclerosis Research
June 15, 2020
RNA sequencing studies of thousands of post mortem human brain samples have generated massive datasets for use in medical research. These studies implicate many different
Introduction Researchers are developing novel, safer treatments for cancer, but bringing new oncology therapies to market is challenging. This white paper will examine the…
Introduction As global obesity rates continue to rise, the search for effective treatments is more critical than ever. Obesity is associated with an increased…
Introduction Changes in how clinical trials are managed in the European Union (EU), mandated by the European Union Clinical Trial Regulation 536/2014 (EU CTR),…
NEWARK, Del.—(BUSINESS WIRE)—QPS India, a subsidiary of QPS Holdings, LLC (QPS), a GLP/GCP-compliant global full-service Contract Research Organization, has achieved another significant milestone by…
TAIPEI, Taiwan—(BUSINESS WIRE)—QPS, a leading global contract research organization (CRO) specializing in preclinical and clinical drug development services, is pleased to announce the expansion…
QPS India has achieved another significant milestone by successfully completing a scheduled inspection by the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) from…