Gene Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a major global health concern: the devastating neurodegenerative disorder is responsible for 60-80 percent of all cases of dementia, and it affects

Alzheimer’s disease is a major global health concern: the devastating neurodegenerative disorder is responsible for 60-80 percent of all cases of dementia, and it affects

Moderna has announced positive interim results from the Phase III trial of its updated mRNA-1010 influenza vaccine. The company reported that the vaccine met all
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder with no known cure. Current treatment options are limited, aiming to alleviate some symptoms through a combination of

For the first time, scientists have genetically engineered fruit flies to undergo parthenogenesis, also known as virgin birth or asexual reproduction. The research, published in
Gene therapy continues to emerge as a promising approach in the treatment and prevention of a wide range of disorders and diseases. Central to the
Gene therapy has revolutionized the field of medical research by offering potential treatments for genetic disorders and diseases previously considered untreatable or incurable. A key
Gene therapies have ushered in a new era of medical possibilities, offering hope to patients with previously untreatable conditions. Their high costs, however, have raised

Ongoing developments in gene therapy continue to demonstrate its potential to transform the global healthcare system. Gene therapies may be the key to unlocking treatments
eGenesis, a biotech company in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is experimenting in the field of xenotransplantation by transplanting gene-edited pig hearts into infant baboons. The company’s goal

Gene therapy focuses on preventing or curing genetic conditions by manipulating the genetic material in living cells. For people with certain medical conditions, gene therapy
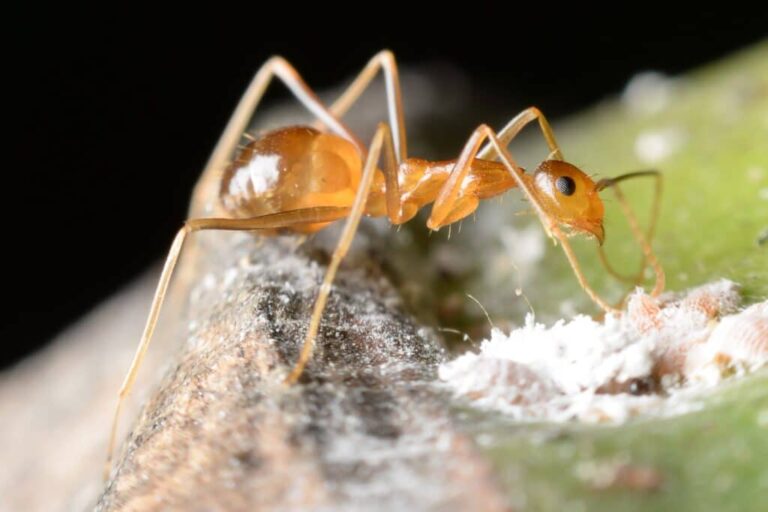

Yellow crazy ants are known for their frenzied movements following disturbances. While this interesting feature is what gave them their name, a groundbreaking international study
Gene therapy holds great promise for the treatment of a wide range of diseases and conditions. By manipulating the genetic material within cells, gene therapy

Alzheimer’s disease is a major global health concern: the devastating neurodegenerative disorder is responsible for 60-80 percent of all cases of dementia, and it affects

Moderna has announced positive interim results from the Phase III trial of its updated mRNA-1010 influenza vaccine. The company reported that the vaccine met all

Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder with no known cure. Current treatment options are limited, aiming to alleviate some symptoms through a combination of

For the first time, scientists have genetically engineered fruit flies to undergo parthenogenesis, also known as virgin birth or asexual reproduction. The research, published in

Gene therapy continues to emerge as a promising approach in the treatment and prevention of a wide range of disorders and diseases. Central to the

Gene therapy has revolutionized the field of medical research by offering potential treatments for genetic disorders and diseases previously considered untreatable or incurable. A key

Gene therapies have ushered in a new era of medical possibilities, offering hope to patients with previously untreatable conditions. Their high costs, however, have raised

Ongoing developments in gene therapy continue to demonstrate its potential to transform the global healthcare system. Gene therapies may be the key to unlocking treatments

eGenesis, a biotech company in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is experimenting in the field of xenotransplantation by transplanting gene-edited pig hearts into infant baboons. The company’s goal

Gene therapy focuses on preventing or curing genetic conditions by manipulating the genetic material in living cells. For people with certain medical conditions, gene therapy

Yellow crazy ants are known for their frenzied movements following disturbances. While this interesting feature is what gave them their name, a groundbreaking international study

Gene therapy holds great promise for the treatment of a wide range of diseases and conditions. By manipulating the genetic material within cells, gene therapy
Delaware Technology Park,
3 Innovation Way,
Newark, DE 19711
"*" indicates required fields

Emails are serviced by Constant Contact. You can revoke your consent to receive emails at any time by using the SafeUnsubscribe® link, found at the bottom of every email.