Hacking the Nervous System to Improve Cancer Treatment
The relationship between cancer and the nervous system has been a curiosity and mystery for nearly two centuries. Jean Cruveilhier’s initial observations in the early

The relationship between cancer and the nervous system has been a curiosity and mystery for nearly two centuries. Jean Cruveilhier’s initial observations in the early

NodThera, a biotech company based in Cambridge, England, is developing a new class of medicines that inhibit the NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3
Annual flu shots in the United States are going to be made a little differently this year, as one of the flu strains usually included

As GLP-1 receptor agonist injections continue to gain acceptance as effective solutions for weight management and cardiovascular health, a tiny drug-delivering implant from Vivani Medical
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), commonly experienced by military personnel, often incur deep damage and invisible scars. Such injuries are significant contributors to post-traumatic stress disorder
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are arguably the hottest topic in medical innovation. The drugs semaglutide and tirzepatide, known under brand names like Ozempic, Wegovy,
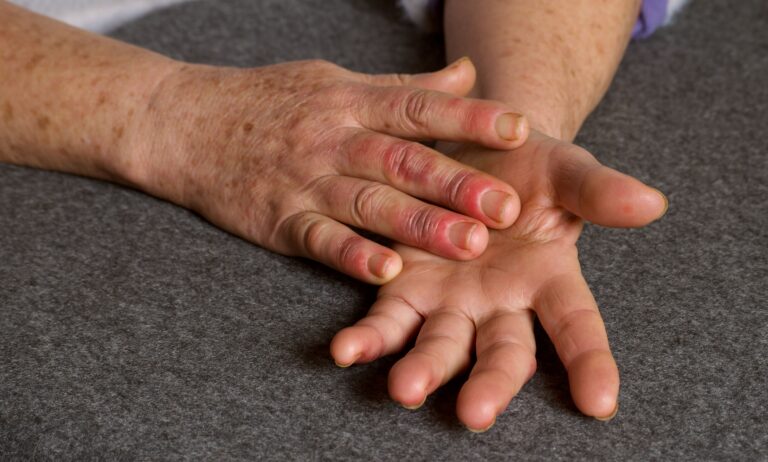
For decades, the battle against autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes, lupus, and multiple sclerosis has been an uphill struggle. Conventional treatments most often alleviate

Research using data from a large U.S. health survey has disrupted conventional thinking about body mass index (BMI) and its role in predicting all-cause mortality.

When a human virus was identified as the source of a 2017 respiratory disease outbreak among chimps at Uganda’s Kibale National Park, the discovery shed
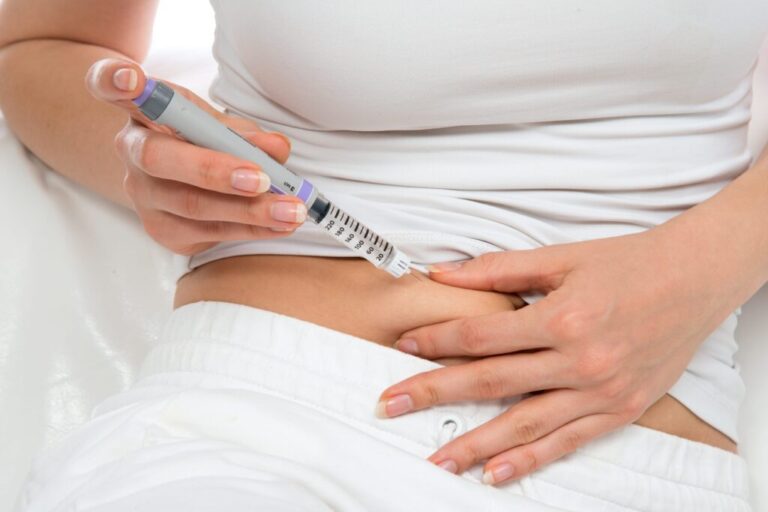
Recent headlines have been abuzz with the groundbreaking weight loss results achieved with the injectable drug semaglutide, demonstrating the potential for people with obesity to
Clinical trial data has demonstrated that the anti-obesity drug semaglutide, marketed for obesity and diabetes, could offer substantial protection against heart disease. The results could
The global effort to eradicate wild poliovirus has made significant strides. Type 2 was declared eradicated in 2015 and type 3 in 2019. Only type

The relationship between cancer and the nervous system has been a curiosity and mystery for nearly two centuries. Jean Cruveilhier’s initial observations in the early

NodThera, a biotech company based in Cambridge, England, is developing a new class of medicines that inhibit the NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3

Annual flu shots in the United States are going to be made a little differently this year, as one of the flu strains usually included

As GLP-1 receptor agonist injections continue to gain acceptance as effective solutions for weight management and cardiovascular health, a tiny drug-delivering implant from Vivani Medical

Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), commonly experienced by military personnel, often incur deep damage and invisible scars. Such injuries are significant contributors to post-traumatic stress disorder

Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are arguably the hottest topic in medical innovation. The drugs semaglutide and tirzepatide, known under brand names like Ozempic, Wegovy,

For decades, the battle against autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes, lupus, and multiple sclerosis has been an uphill struggle. Conventional treatments most often alleviate

Research using data from a large U.S. health survey has disrupted conventional thinking about body mass index (BMI) and its role in predicting all-cause mortality.

When a human virus was identified as the source of a 2017 respiratory disease outbreak among chimps at Uganda’s Kibale National Park, the discovery shed

Recent headlines have been abuzz with the groundbreaking weight loss results achieved with the injectable drug semaglutide, demonstrating the potential for people with obesity to

Clinical trial data has demonstrated that the anti-obesity drug semaglutide, marketed for obesity and diabetes, could offer substantial protection against heart disease. The results could

The global effort to eradicate wild poliovirus has made significant strides. Type 2 was declared eradicated in 2015 and type 3 in 2019. Only type
Delaware Technology Park,
3 Innovation Way,
Newark, DE 19711
"*" indicates required fields

Emails are serviced by Constant Contact. You can revoke your consent to receive emails at any time by using the SafeUnsubscribe® link, found at the bottom of every email.